
Jan. 27, 2020
Program News
OSIRIS-REx Completes Closest Flyover of Sample Site Nightingale
From the OSIRIS-REx mission:
Preliminary results indicate that NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft successfully executed a 0.4-mile (620-m) flyover of site Nightingale yesterday as part of the mission’s Reconnaissance B phase activities. Nightingale, OSIRIS-REx’s primary sample collection site, is located within a crater high in asteroid Bennu’s northern hemisphere.
To perform the pass, the spacecraft left its 0.75-mile (1.2-km) safe home orbit and flew an almost 11-hour transit over the asteroid, aiming its science instruments toward the 52-ft (16-m) wide sample site before returning to orbit. Science observations from this flyover are the closest taken of a sample site to date.
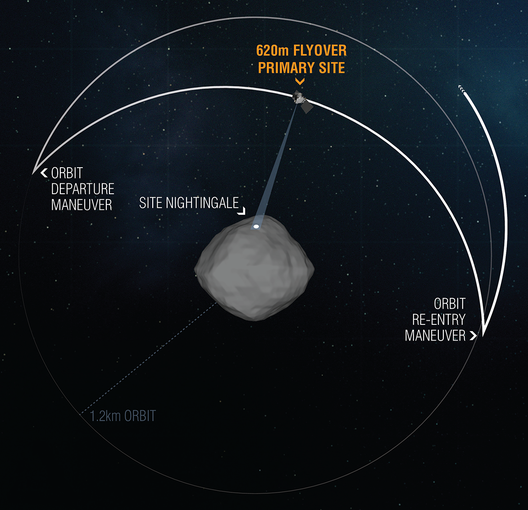
During the Recon B flyover of primary sample collection site Nightingale, OSIRIS-REx left its safe-home orbit to fly over the sample site at an altitude of 0.4 miles (620 m). The pass, which took around 11 hours, gave the spacecraft’s onboard instruments the opportunity to take the closest-ever science observations of the site.Image credit: NASA/Goddard/University of Arizona.
The primary goal of the Nightingale flyover was to collect the high-resolution imagery required to complete the spacecraft’s Natural Feature Tracking image catalog, which will document the sample collection site’s surface features – such as boulders and craters. During the sampling event, which is scheduled for late August, the spacecraft will use this catalog to navigate with respect to Bennu’s surface features, allowing it to autonomously predict where on the sample site it will make contact . Several of the spacecraft’s other instruments also took observations of the Nightingale site during the flyover event, including the OSIRIS-REx Thermal Emissions Spectrometer (OTES), the OSIRIS-REx Visual and InfraRed Spectrometer (OVIRS), the OSIRIS-REx Laser Altimeter (OLA), and the MapCam color imager.
A similar flyover of the backup sample collection site, Osprey, is scheduled for Feb. 11. Even lower flybys will be performed later this spring – Mar. 3 for Nightingale and May 26 for Osprey – as part of the mission’s Reconnaissance C phase activities. The spacecraft will perform these two flyovers at an altitude of 820 feet (250 m), which will be the closest it has ever flown over asteroid Bennu’s surface.
Click here to read the full article from the OSIRIS-REx mission site.
NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) spacecraft is the first U.S. mission to return samples from an asteroid to Earth, addressing multiple NASA Solar System Exploration objectives. OSIRIS-REx launched from Cape Canaveral at 7:05 p.m. EDT on September 8, 2016. OSIRIS-REx completed its 1.2 billion-mile (2 billion-kilometer) journey to arrive at the asteroid Bennu on December 3, 2018.