In a new paper, NASA-supported scientists have predicted that there is an Earth-sized planet in the habitable zone of the star SPECULOOS-2. Moreover, this planet would have finished its formation process within the habitable zone and it could be one of the most Earth-like planets yet identified.
Astrobiologists are very interested in identifying stars that host planets orbiting within their habitable zone (the distance at which the energy from a star is just right to support liquid water on a planet’s surface). Finding planets that are similar in size to the Earth and in a habitable zone could be the first step in locating a distant world that could support life as we know it. Discovering systems that host such worlds will help narrow down the search for habitable exoplanets, and could identify planets to be studied in more detail with powerful instruments like the Webb space telescope.
This illustration shows two Earth-sized worlds passing in front of their parent red dwarf star, which is much smaller and cooler than our sun.Image credit: NASA/ESA/J. de Wit (MIT)/G. Bacon (STScI).
The TRAPPIST-1 system is one example where Earth-sized planets are known to orbit in the star’s habitable zone. However, it is thought that these planets were not always located in this region, and instead they migrated to their host star’s habitable zone after their formation. This is different from what is believed to have happened with the Earth. Scientists believe that the Earth has always been in the habitable zone of the Sun, allowing billions of years in which life could originate and evolve.
In 2019, the Search for habitable Planets EClipsing ULtra-cOOl Stars (SPECULOOS) project began operating with the goal of identifying planets whose atmospheres could be suitable targets for characterization by the Webb telescope. This year, astronomers with the project announced the discovery of two super-Earths (rocky planets larger than Earth) orbiting in the habitable zone of a dim red dwarf star called SPECULOOS-2.
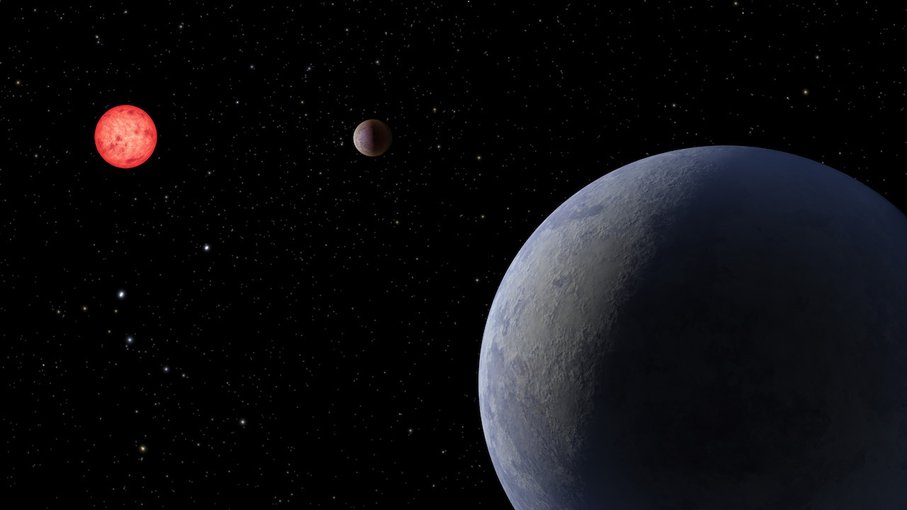

Artist illustration of another super-Earth discovered this year around the star LP 890-9. The image shows the planet, dubbed LP 890-9 c, in the foreground and its sister planet, LP 890-9 b, orbiting a red-dwarf star some 98 light-years away from Earth.Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech.
A new study is now providing more details about the SPECULOOS-2 system, and whether or not there are any other planets orbiting the star that might be better candidates for habitability. By modeling the architecture of the system, scientists predict that there is an Earth-sized planet in the habitable zone and, importantly, this planet has been sitting in the habitable zone since the early days of its formation. If astronomers are able to confirm the presence of this potential planet, it could be an excellent candidate for future astrobiology studies.
The study, “Prediction of an Earth-sized Planet Formed in the Habitable Zone of the SPECULOOS-2 System,” was published in Research Notes of the American Astronomical Society (AAS). The study was performed by members of the Nexus for Exoplanet System Science (NExSS), a NASA research coordination network (RCN) dedicated to the study of planetary habitability.
Related:
Discovery Alert: A Rocky ‘Super-Earth’ in the Habitable Zone (NASA)
Promising Worlds Found Around Nearby Ultra-cool Dwarf Star (NASA)
