2011 Annual Science Report
 University of Wisconsin
Reporting | SEP 2010 – AUG 2011
University of Wisconsin
Reporting | SEP 2010 – AUG 2011
Executive Summary
The focus of the WARC Team is on the signatures and environments of life, and in Year 4, the team significantly expanded its research and Education and Public Outreach (EPO) efforts into new directions within this framework. Twenty-six research projects were pursued in Year 4, including 15 continuing projects and 11 new initiatives. EPO efforts in Year 4 also expanded, and ten major projects and programs were run through NASA-JPL and the University of Wisconsin.
Research Topic 1: Early surface conditions on Mars and Earth – Implications for Life
Four entirely new research projects for WARC were pursued in Year 4 that were aimed at determining the environments that existed on Mars and Earth between ~4.0 and 3.5 Ga, as well as the role that core formation has in providing conditions favorable to supporting life. WARC research in the previous year provided the first rigorous igneous crystallization age for Mars meteorite ALH84001 by Lu-Hf geochronology, and in Year 4, Brian Beard’s group applied the Rb-Sr isotope system to studying the carbonates contained in ALH84001. Beard found that the meteorite experienced a shock event at 3951±22 Ma, significantly younger than the igneous crystallization age of 4091±30 Ma determined by Lu-Hf, and, based on petrographic relations, the shock age is interpreted to be the carbonate formation age. Importantly, the initial 87Sr/86Sr ratio for the carbonates and associated minerals is very high, requiring a surface environment high in Rb/Sr, most likely reflecting clays on the surface of Mars at ~4 Ga. Turning to early Archean terrestrial rocks, Clark Johnson led two studies in Year 4 that combined U-Th-Pb geochronology with Fe isotope measurements on the 3.4 Ga Apex Basalt and Marble Bar Chert from the Pilbara craton, Australia. It has been previously hypothesized that ferric iron minerals in these units reflect oxidation by free oxygen at ~3.4 Ga, which, if true, should have been accompanied by an ancient enrichment in U, given the high solubility of U(VI). By coupling the 238U-206Pb and 235U-207Pb isotope systems, and referencing to the immobile and non-redox-sensitive 232Th-208Pb isotope systems, Johnson and colleagues showed that the 3.4 Ga rocks from the Pilbara craton were not associated with ancient U enrichment and hence are unlikely to record oxygen-rich early Archean conditions. Moreover, Fe isotope analyses of the Marble Bar jaspers showed the highest δ56Fe values yet measured on Earth, indicating oxidation under conditions of very limited oxidant, supporting the interpretation that no free oxygen existed on Earth at this time; the data are instead interpreted to reflect oxidation by anoxygenic phototrophs, a metabolism that is deeply rooted and therefore likely to have occurred early in Earth’s history.
Finally, Max Coleman led a study in Year 4 that investigated the effect of core evolution on Earth’s magnetic field, which bears on the extent of magnetic shielding of cosmic radiation, which in turn has implications for the evolution of life. Coleman’s group hypothesized that extensive magnetic shielding likely occurred only after turbulent flow in the liquid outer core subsided, which would have been after 1 or 2 b.y. of inner core solidification that allowed differential rotation of the inner and outer core. These results suggest that life which evolved in the first 1 to 2 b.y. of Earth history would have had to develop strategies to cope with high cosmic radiation.
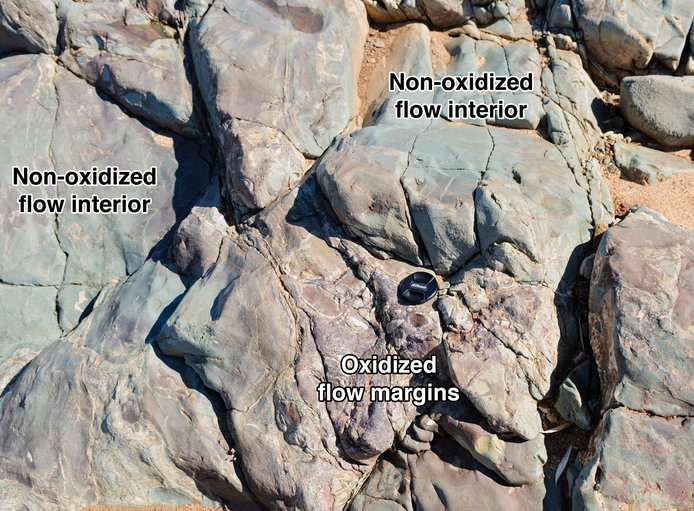
Figure 1. 3.4 Ga Apex Basalt, Pilbara Craton, Australia. The fractured flow margins of the lavas flows have been oxidized (pink color), whereas the interiors of individual flows have not been oxidized (green color). Some workers have interpreted the oxidation to reflect interaction with oxygenated seawater at 3.4 Ga. New work shows that oxidation occurred in the Phanerozoic and not the early Archean.
Research Topic 2: Organic compounds in the terrestrial planets – Inventories, evolution, and survivability
Organic compounds are, of course, the building blocks of life, and WARC research in Year 4 on organic material covered a broad range of topics. Five projects were pursued, including one new project aimed at in situ C isotope analysis of microfossils. Nita Sahai led a continuing investigation of the delivery of pre-biotic amino acids to the early Earth based on studies of carbonaceous chondrites, with a focus on factors that may determine chirality, based on observations that amino acids in some meteorites exhibit significant asymmetry in chirality. Observations from meteorites were compared with mineral absorption studies, and no chiral preference was shown during sorption, indicating that the chiral asymmetry observed in some meteorites cannot reflect condensation or sorption processes. In a second continuing project led by Sahai, the role of mineral surfaces in stabilizing lipid membranes as possible “proto cells” was investigated. Sahai’s group found that lipid membrane stability in the presence of minerals is highly variable, dependent upon surface charge, solution chemistry, and mineral particle size. This on-going work hopes to constrain the conditions required to promote development of “proto cells”, which in turn can inform models for the early evolution of life. A third project led by Sahai continued studies of the role of extra-cellular polymeric substances (EPS) as a possible strategy for early life in dealing with toxic mineral surfaces. The results to date provide evidence that EPS, and biofilms in general, may have evolved as a means for protecting microbial communities from toxic effects of mineral substrates, in addition to the traditional interpretation that such substances developed to provide physical stabilization of microbial communities on rocky substrates. In Year 4, John Valley’s team began a new project on carbon isotope analysis by SIMS (Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry), initially concentrating on methods and standard development, a critical aspect given the large ranges in carbon abundances in rocks. Valley’s group demonstrated that high-precision C isotope data can be obtained on sub-components of cells, and showed that fossil cell walls and interiors may have distinct isotopic compositions in samples of 2.7 to 3.4 Ga age. The fifth component of research related to organic compounds in Year 4 was a continuation of the EXPOSE-R studies led by Pascale Ehrenfreund, where samples were exposed to space radiation on the International Space Station (ISS). Samples were returned to Earth in Year 4 of the grant, providing a total exposure to space radiation that greatly exceeded that previously obtained in laboratory experiments. Full analysis of these experiments will occur in Year 5 of the grant and will provide a rigorous evaluation of the effects of space exposure of organic compounds.
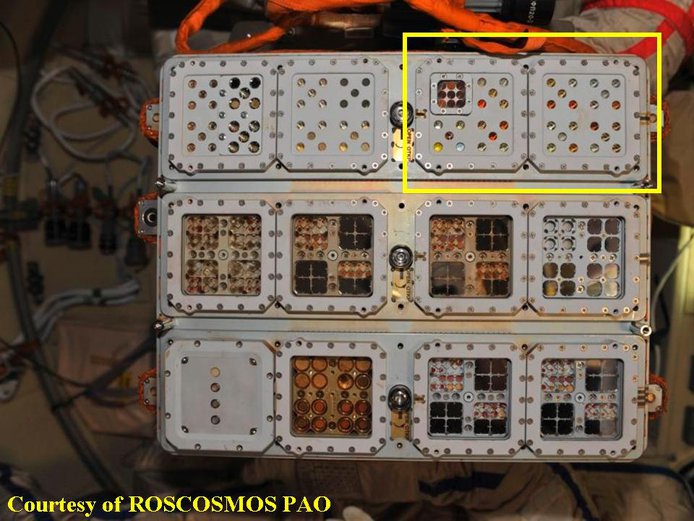
Figure 2. EXPOSE-R retrieved by EVA in January 2011. The yellow box depicts the Organic experiment. The fluorescent color of PAH and fullerenes witnesses that degradation has not destroyed the entire sample.
Research Topic 3: The transition to an oxygenated Earth
Three research projects pursued in Year 4 targeted the biogeochemical changes in the rock record that mark the transition to an oxygenated Earth. Valley’s group continued two studies that involved SIMS stable isotope analysis, one focussed on O and Si isotopes in 2.5 Ga (and older) Banded Iron Formations (BIFs), and a second aimed at multiple S isotopes in 2.4 Ga rocks that immediately preceded the Great Oxidation Event (GOE). SIMS analysis demonstrated extremely large ranges in O isotope compositions, particularly for oxide minerals, that likely reflect unique formation pathways and hydrothermal histories; such information would not be attainable by conventional bulk isotopic analyses, and demonstrate that near-primary isotopic compositions may be recovered by careful SIMS analysis. Silicon isotopes were shown to be relatively insensitive to the effects of metamorphism, demonstrating promise for distinguishing continental, hydrothermal, and biological pathways involved in Si cycling in BIFs. Turning to multiple S isotopes in rocks deposited immediately before the GOE, Valley’s team documented an extremely large range in mass-dependent S isotope variations on the microscale, indicating that dissimilatory sulfate reduction was active at this time. These results contrast with the wide range in mass-independent S isotope variations found in the same analyses, which suggests that overall atmospheric oxygen contents remained low. These rocks, therefore, probably capture a condition at 2.4 Ga where significant seawater sulfate existed while atmospheric oxygen contents remained low. Finally, Clark Johnson’s group pursued an integrated isotopic study of the Neoarchean Campbellrand carbonate platform, South Africa, continuing their work from the previous year, where new datasets for C, O, Fe, and Sr isotopes were integrated with existing data for S and Mo isotopes. These data provide a detailed view of the paleoenvironmental and paleoecological conditions of the Neoarchean, including which types of samples record ambient marine conditions, and which are dominated by microbial cycling after deposition. Collectively, the dataset provides strong evidence for free oxygen in the photic zone of the oceans between 2.7 and 2.5 Ga, generated by oxygenic photosynthesis, but little free oxygen in the atmosphere. Moreover, the results demonstrate that, in general, BIFs are dominated by post-depositional microbial Fe cycling, and few of the isotopic compositions of BIFs can be traced to ambient marine conditions. In contrast, shallow-water Ca-Mg carbonates, unless altered, faithfully record ambient marine conditions in the photic zone.
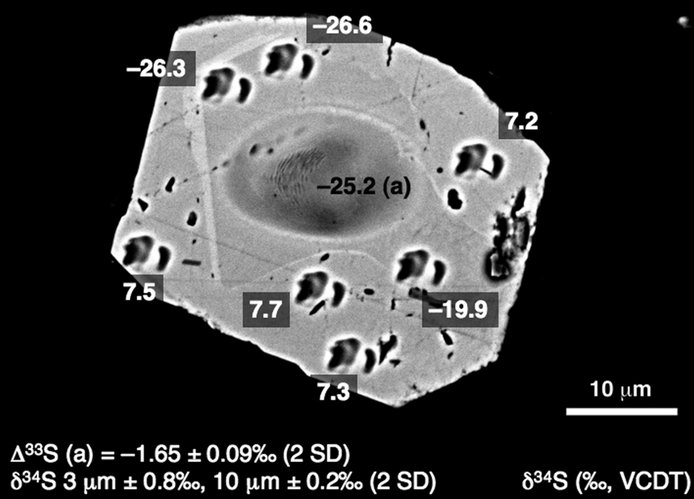
Figure 3. Backscattered electron image of a pyrite grain from the Meteorite Bore Member showing large (~10 mm, δ34S and Δ33S) and small (~3 mm, δ34S) SIMS analytical pits and sulfur isotope compositions. Subhedral original grain with low δ34S was overgrown by a euhedral rim with high δ34S (after Williford et al. 2011).
Research Topic 4: Life detection in the rock record I – Iron oxides
Eric Roden’s team led three investigations aimed at understanding the biosignatures that may be left in the rock record by microbial Fe cycling, including one project that is new for Year 4. The first project investigated the ability of Fe(II)-oxidizing, chemolithotrophic microorganisms to live on Fe(II)-bearing igneous minerals, as well as clays. Roden’s group found that a wide variety of Proteobacteria are capable of catalyzing solid-phase Fe(II), including many species not previously known to have this capability. These results bear on the possibility that early life on Mars, when Fe(II)-clays may have been abundant, could have used this metabolic pathway. A second project investigated stable iron isotope fractionations in abiological and biological systems involving Si-bearing ferrihydrite and aqueous Fe(II). This system was chosen because the Precambrian oceans were likely saturated in silica, and the Archean oceans likely had significant quantities of Fe(II). These experiments showed that Fe isotope exchange is enhanced in biological systems, likely reflecting the close proximity of aqueous Fe(II) that is produced by in situ reduction of Fe(III), in contrast to simple juxtaposition of Fe(II) and Fe(III) hydroxides in abiologic systems. A new project for Year 4 involved a field study where biogenic magnetite forms via dissimilatory iron reduction. At the field site, iron reduction runs essentially to completion, producing little Fe isotope variability in the samples. This contrasts with the large Fe isotope variations measured at other field sites where iron reduction is incomplete, providing an interpretive framework for studies of the ancient rock record in terms of fine-scale Fe isotope variability.
Research Topic 5: Life detection in the rock record II – carbonates
A major focus of Year 4 research on biosignatures involved carbonate minerals, and six projects were pursued in Year 4, three of which were new. Chris Romanek’s group continued their extensive series of abiologic synthesis experiments using free-drift and chemostat approaches, where calcite seed crystals were used to nucleate growth of Mg-bearing carbonates. Romanek’s team was able to produce a wide range of carbonate compositions through changes in experimental conditions, and they demonstrated that the use of seed crystals, which reduce nucleation energy barriers to carbonate precipitation, are an effective means for growing carbonate under near-equilibrium conditions. The experiments done in Romanek’s lab were used for stable Mg isotope analysis, a second project, new for Year 4, led by Brian Beard. Beard’s team found that the stable Mg isotope compositions of Mg-calcite were independent of carbonate composition, and that the fractionation between Mg in solution and calcite was mildly dependent on temperature. The isotopic fractionations appear to follow an equilibrium relation, providing the first rigorously determined stable Mg isotope fractionation factors for carbonates. These results demonstrate the promise of stable Mg isotope geochemistry for determining the origin of carbonates, as well as the Mg isotope composition of seawater, which may eventually find use as a proxy for continental weathering. Huifang Xu led a new experimental study that tested the hypothesis that sulfide catalyzes dewatering of Mg in solution, therefore promoting dolomite formation. Xu’s team found that even small amounts of sulfide promoted dolomite formation. In contrast, Nita Sahai’s group found, via computational approaches, that aqueous sulfide is an unlikely mechanism for Mg dehydration, in apparent conflict with the experimental results. A possible reconciliation of the new computational results and experiments may lie in the effect of sulfide at the surface of an amorphous carbonate precursor, and this will be pursued in future work. Xu additionally pursued two studies aimed at understanding the possible role of biological ligands in promoting dolomite precipitation. The first study was a continuation of work in the previous year that investigated production of disordered dolomite in experiments that used agar gel, as well as halophilic bacteria, which, upon annealing at elevated temperature, converted to true dolomite. The second study, new for Year 4, produced protodolomite using extracellular polysaccharides, which are excreted by many microorganisms. Collectively, the two studies suggest that biological ligands can indeed catalyze dolomite formation, suggesting that the presence of dolomite in the rock record may, by itself, implicate life.
Research Topic 6: Mars analog environments
Research on Mars analog environments continued to be an important mission-related component of work in Year 4, and two projects were pursued. Pascale Ehrenfreund continued research on Mars analog field sites, including the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS) in Utah. A major finding of this work was that “life detection” approaches may yield dramatically different results depending upon the instrumentation and methodology used. For example, on-site Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) identified several microbial domains at MDRS, but amino acid and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) measurements were highly variable. Soil samples had a great diversity of mineralogy, including highly reactive clays and oxides, suggesting that sorption of PAH and amino acids may inhibit traditional approaches to life detection, masking the presence of microbial populations that PCR indicates are clearly present. Max Coleman led a second project, a continuation of work on Rio Tinto, Spain, a locality where oxidative weathering of pyrite produces highly acidic waters and a wide variety of ferric oxides and sulfates, analogous to ancient Mars environments inferred by the Mars Exploration Rovers. A key issue in understanding the biogeochemical pathways involved in pyrite oxidation is the source of oxygen in sulfate, be it from water or the atmosphere, and Coleman’s team showed that measurement of three stable isotopes of oxygen (16O, 17O, and 18O) have the potential for discriminating between biological and abiological pathways, as well as the source of oxygen in sulfate.
Figure 4. Rio Tinto, Spain, represents a Mars analog environment, reflecting the acidic conditions of sulfur and iron oxidation that may have existed on early Mars. Left photo shows green waters at Rio Tinto that contain reduced ferrous iron, and right photo shows waters that contain red oxidized iron.
Research Topic 7: New technologies for astrobiology
Three projects were pursued in Year 4 that were focussed on developing new technologies for astrobiology, ranging from new ways to explore the surface of Mars to establishing the micro-analytical methods that will be required for sample return missions from Mars. Max Coleman’s group led a new initiative that explored the use of Tumbleweed rovers for exploring the surface of Mars. These vehicles are designed to migrate randomly over the Mars surface, propelled by transient wind, therefore using minimal power. In addition, Tumbleweed rovers may be built for significantly less cost than traditional rovers, allowing large areas of the landscape to be covered. Mahadeva Sinha continued work on developing a Miniature Mass Spectrometer (MMS) for deployment on Mars, which would be capable of chemical and isotopic analysis via laser ablation. The unique capabilities of the MMS include a 100 % duty cycle, and high sensitivity due to the use of neutral species for analysis via electron-impact ionization. A new focus for the development of the MMS in Year 4 was K-Ar geochronology, which should have widespread applications on Mars as a means for screening samples for sample return missions. A third project was directed by John Valley, which continued development work for high-precision stable isotope measurements using Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS). Work continued on O and S isotope analysis, where Valley’s team has developed strategies for dealing with crystal orientation effects that are now known to affect SIMS analysis for certain minerals. In addition, in Year 4 Valley’s group began work on the protocols required for SIMS analysis of carbon isotopes in organic material, including individual microfossils, which presents very significant challenges.
Education and Public Outreach (EPO) activities
The EPO portfolio was significantly expanded in Year 4 with ten projects and programs, divided between NASA-JPL and the University of Wisconsin – Madison. Kay Ferrari (JPL) continued her work with the Solar System Educator (SSE) and Solar System Ambassador (SSA) events, which included an online SSE astrobiology training program through a nationwide website, SSE workshops that reached over 1,500 teachers, and SSA events that reached over 300,000 people. In addition, a SSE workshop was held at the Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference in Year 4. Additional EPO activities centered at JPL included Space Day for more than 250 K-8 students in the Los Angeles area, and participation in an undergraduate summer internship program at JPL, in collaboration with Max Coleman. Brooke Norsted (UW-Madison) continued work on the Imagine Mars program, expanding into new schools in Year 4. In addition, a new initiative, “Astrobiology in Your Backyard” was started in Year 4, which was brought to three summer music festivals. Other UW-Madison EPO activities included publication of the NASA-sponsored “Life in the Extreme Trading Cards”, and completion of the first phase of a permanent astrobiology exhibit in the Geology Museum.
Figure 5. Educators Engaged at ASP Conference Astrobiology Convocation Workshop.
Figure 6. Left photo: Post-doc Andy Czaja staffs the “Astrobiology in Your Backyard” booth at a Madison, WI music festival in Summer 2011. Right photo: Post-doc Ken Williford looks on as Akira Toki middle school students operate the hydroponic system they built during the Imagine Mars after school science club.
Publications
-
FERNÁNDEZ-REMOLAR, D. C., SÁNCHEZ-ROMÁN, M., Hill, A. C., GÓMEZ-ORTÍZ, D., Ballesteros, O. P., Romanek, C. S., & Amils, R. (2011). The environment of early Mars and the missing carbonates. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 46(10), 1447–1469. doi:10.1111/j.1945-5100.2011.01238.x
-
Ansdell, M., Ehrenfreund, P., & McKay, C. (2011). Stepping stones toward global space exploration. Acta Astronautica, 68(11-12), 2098–2113. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2010.10.025
-
Beard, B. L., Ludois, J. M., Lapen, T. J., & Johnson, C. M. (2013). Pre-4.0 billion year weathering on Mars constrained by Rb–Sr geochronology on meteorite ALH84001. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 361, 173–182. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.10.021
-
Bramall, N. E., Quinn, R., Mattioda, A., Bryson, K., Chittenden, J. D., Cook, A., … Hoffmann, S. V. (2012). The development of the Space Environment Viability of Organics (SEVO) experiment aboard the Organism/Organic Exposure to Orbital Stresses (O/OREOS) satellite. Planetary and Space Science, 60(1), 121–130. doi:10.1016/j.pss.2011.06.014
-
Bryson, K. L., Peeters, Z., Salama, F., Foing, B., Ehrenfreund, P., Ricco, A. J., … Robert, F. (2011). The ORGANIC experiment on EXPOSE-R on the ISS: Flight sample preparation and ground control spectroscopy. Advances in Space Research, 48(12), 1980–1996. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2011.07.017
-
Cloutis, E. A., Hudon, P., Romanek, C. S., Bishop, J. L., Reddy, V., Gaffey, M. J., & Hardersen, P. S. (2010). Spectral reflectance properties of ureilites. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 45(10-11), 1668–1694. doi:10.1111/j.1945-5100.2010.01065.x
-
Cox, N. L. J., Ehrenfreund, P., Foing, B. H., D’Hendecourt, L., Salama, F., & Sarre, P. J. (2011). Linear and circular spectropolarimetry of diffuse interstellar bands. A&A, 531, A25. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201016365
-
Czaja, A. D., Johnson, C. M., Roden, E. E., Beard, B. L., Voegelin, A. R., Nägler, T. F., … Wille, M. (2012). Evidence for free oxygen in the Neoarchean ocean based on coupled iron–molybdenum isotope fractionation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 86, 118–137. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.007
-
Czaja, A. D., Johnson, C. M., Yamaguchi, K. E., & Beard, B. L. (2012). Comment on “Abiotic Pyrite Formation Produces a Large Fe Isotope Fractionation”. Science, 335(6068), 538–538. doi:10.1126/science.1211804
-
Direito, S. O. L., Ehrenfreund, P., Marees, A., Staats, M., Foing, B., & Röling, W. F. M. (2011). A wide variety of putative extremophiles and large beta-diversity at the Mars Desert Research Station (Utah). International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 191–207. doi:10.1017/s1473550411000012
-
Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). A Multiple-Choice Essay. Astrobiology, 11(8), 737–741. doi:10.1089/ast.2011.0697
-
Ehrenfreund, P., & Foing, B. H. (2010). Fullerenes and Cosmic Carbon. Science, 329(5996), 1159–1160. doi:10.1126/science.1194855
-
Ehrenfreund, P., McKay, C., Rummel, J. D., Foing, B. H., Neal, C. R., Masson-Zwaan, T., … Race, M. (2012). Toward a global space exploration program: A stepping stone approach. Advances in Space Research, 49(1), 2–48. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2011.09.014
-
Ehrenfreund, P., Röling, W. F. M., Thiel, C. S., Quinn, R., Sephton, M. A., Stoker, C., … Foing, B. H. (2011). Astrobiology and habitability studies in preparation for future Mars missions: trends from investigating minerals, organics and biota. International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 239–253. doi:10.1017/s1473550411000140
-
Foing, B. H., Stoker, C., Zavaleta, J., Ehrenfreund, P., Thiel, C., Sarrazin, P., … Davies, G. R. (2011). Field astrobiology research in Moon–Mars analogue environments: instruments and methods. International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 141–160. doi:10.1017/s1473550411000036
-
Halasinski, T. M., Ruiterkamp, R., Salama, F., Foing, B. H., & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). C 84 : A Prototype of Larger Fullerenes. Laboratory Spectroscopy and Astronomical Relevance. Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures, 19(5), 398–409. doi:10.1080/15363831003721807
-
Heck, P. R., Huberty, J. M., Kita, N. T., Ushikubo, T., Kozdon, R., & Valley, J. W. (2011). SIMS analyses of silicon and oxygen isotope ratios for quartz from Archean and Paleoproterozoic banded iron formations. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(20), 5879–5891. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2011.07.023
-
Hong, K-S., Xu, H., Konishi, H., & Li, X. (2010). Direct Water Splitting Through Vibrating Piezoelectric Microfibers in Water. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 1(6), 997–1002. doi:10.1021/jz100027t
-
Huberty, J. M., Kita, N. T., Kozdon, R., Heck, P. R., Fournelle, J. H., Spicuzza, M. J., … Valley, J. W. (2010). Crystal orientation effects in δ18O for magnetite and hematite by SIMS. Chemical Geology, 276(3-4), 269–283. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.06.012
-
Huberty, J. M., Konishi, H., Heck, P. R., Fournelle, J. H., Valley, J. W., & Xu, H. (2012). Silician magnetite from the Dales Gorge Member of the Brockman Iron Formation, Hamersley Group, Western Australia. American Mineralogist, 97(1), 26–37. doi:10.2138/am.2012.3864
-
Jimenez-Lopez, C., Rodriguez-Navarro, C., Rodriguez-Navarro, A., Perez-Gonzalez, T., Bazylinski, D. A., Lauer, H. V., & Romanek, C. S. (2012). Signatures in magnetites formed by (Ca,Mg,Fe)CO3 thermal decomposition: Terrestrial and extraterrestrial implications. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 87, 69–80. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.028
-
Jimenez-Lopez, C., Romanek, C. S., & Bazylinski, D. A. (2010). Magnetite as a prokaryotic biomarker: A review. J. Geophys. Res., 115(G2), n/a–n/a. doi:10.1029/2009jg001152
-
Kita, N. T., Huberty, J. M., Kozdon, R., Beard, B. L., & Valley, J. W. (2010). High-precision SIMS oxygen, sulfur and iron stable isotope analyses of geological materials: accuracy, surface topography and crystal orientation. Surf. Interface Anal., 43(1-2), 427–431. doi:10.1002/sia.3424
-
Kotler, J. M., Quinn, R. C., Foing, B. H., Martins, Z., & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). Analysis of mineral matrices of planetary soil analogues from the Utah Desert. International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 221–229. doi:10.1017/s1473550411000103
-
Kozdon, R., Kita, N. T., Huberty, J. M., Fournelle, J. H., Johnson, C. A., & Valley, J. W. (2010). In situ sulfur isotope analysis of sulfide minerals by SIMS: Precision and accuracy, with application to thermometry of ∼3.5Ga Pilbara cherts. Chemical Geology, 275(3-4), 243–253. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.05.015
-
Li, W., Chakraborty, S., Beard, B. L., Romanek, C. S., & Johnson, C. M. (2012). Magnesium isotope fractionation during precipitation of inorganic calcite under laboratory conditions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 333-334, 304–316. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.04.010
-
Martins, Z., Sephton, M. A., Foing, B. H., & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). Extraction of amino acids from soils close to the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS), Utah. International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 231–238. doi:10.1017/s1473550410000431
-
Nicholson, W. L., Ricco, A. J., Agasid, E., Beasley, C., Diaz-Aguado, M., Ehrenfreund, P., … Young, A. (2011). The O/OREOS Mission: First Science Data from the Space Environment Survivability of Living Organisms (SESLO) Payload. Astrobiology, 11(10), 951–958. doi:10.1089/ast.2011.0714
-
Oleson, T. A., & Sahai, N. (2010). Interaction energies between oxide surfaces and multiple phosphatidylcholine bilayers from extended-DLVO theory. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 352(2), 316–326. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2010.08.056
-
Oleson, T. A., Sahai, N., & Pedersen, J. A. (2010). Electrostatic effects on deposition of multiple phospholipid bilayers at oxide surfaces. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 352(2), 327–336. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2010.08.057
-
Orzechowska, G. E., Kidd, R. D., Foing, B. H., Kanik, I., Stoker, C., & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). Analysis of Mars analogue soil samples using solid-phase microextraction, organic solvent extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 209–219. doi:10.1017/s1473550410000443
-
Orzechowska, G. E., Kidd, R. D., Foing, B. H., Kanik, I., Stoker, C., & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). Analysis of Mars analogue soil samples using solid-phase microextraction, organic solvent extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 209–219. doi:10.1017/s1473550410000443
-
Peeters, Z., Vos, D., Ten Kate, I. L., Selch, F., Van Sluis, C. A., Sorokin, D. Y., … Ehrenfreund, P. (2010). Survival and death of the haloarchaeon Natronorubrum strain HG-1 in a simulated martian environment. Advances in Space Research, 46(9), 1149–1155. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2010.05.025
-
Percak-Dennett, E. M., Beard, B. L., Xu, H., Konishi, H., Johnson, C. M., & Roden, E. E. (2011). Iron isotope fractionation during microbial dissimilatory iron oxide reduction in simulated Archaean seawater. Geobiology, 9(3), 205–220. doi:10.1111/j.1472-4669.2011.00277.x
-
Percak-Dennett, E. M., Loizeau, J-L., Beard, B. L., Johnson, C. M., & Roden, E. E. (2013). Iron isotope geochemistry of biogenic magnetite-bearing sediments from the Bay of Vidy, Lake Geneva. Chemical Geology, 360-361, 32–40. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.10.008
-
Roden, E. E., Kappler, A., Bauer, I., Jiang, J., Paul, A., Stoesser, R., … Xu, H. (2010). Extracellular electron transfer through microbial reduction of solid-phase humic substances. Nature Geosci, 3(6), 417–421. doi:10.1038/ngeo870
-
Romanek, C. S., Morse, J. W., & Grossman, E. L. (2011). Aragonite Kinetics in Dilute Solutions. Aquat Geochem, 17(4-5), 339–356. doi:10.1007/s10498-011-9127-2
-
Sinha, M. P., Neidholdt, E. L., Hurowitz, J., Sturhahn, W., Beard, B., & Hecht, M. H. (2011). Laser ablation-miniature mass spectrometer for elemental and isotopic analysis of rocks. Review of Scientific Instruments, 82(9), 094102. doi:10.1063/1.3626794
-
Sánchez-Román, M., McKenzie, J. A., De Luca Rebello Wagener, A., Romanek, C. S., Sánchez-Navas, A., & Vasconcelos, C. (2011). Experimentally determined biomediated Sr partition coefficient for dolomite: Significance and implication for natural dolomite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(3), 887–904. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2010.11.015
-
Sánchez-Román, M., Romanek, C. S., Fernández-Remolar, D. C., Sánchez-Navas, A., McKenzie, J. A., Pibernat, R. A., & Vasconcelos, C. (2011). Aerobic biomineralization of Mg-rich carbonates: Implications for natural environments. Chemical Geology, 281(3-4), 143–150. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.11.020
-
Tangalos, G. E., Beard, B. L., Johnson, C. M., Alpers, C. N., Shelobolina, E. S., Xu, H., … Roden, E. E. (2010). Microbial production of isotopically light iron(II) in a modern chemically precipitated sediment and implications for isotopic variations in ancient rocks. Geobiology, 8(3), 197–208. doi:10.1111/j.1472-4669.2010.00237.x
-
Thiel, C. S., Ehrenfreund, P., Foing, B., Pletser, V., & Ullrich, O. (2011). PCR-based analysis of microbial communities during the EuroGeoMars campaign at Mars Desert Research Station, Utah. International Journal of Astrobiology, 10(03), 177–190. doi:10.1017/s1473550411000073
-
Vos, D. A. I., Cox, N. L. J., Kaper, L., Spaans, M., & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). Diffuse interstellar bands in Upper Scorpius: probing variations in the DIB spectrum due to changing environmental conditions. A&A, 533, A129. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200809746
-
Williford, K. H., Van Kranendonk, M. J., Ushikubo, T., Kozdon, R., & Valley, J. W. (2011). Constraining atmospheric oxygen and seawater sulfate concentrations during Paleoproterozoic glaciation: In situ sulfur three-isotope microanalysis of pyrite from the Turee Creek Group, Western Australia. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(19), 5686–5705. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2011.07.010
-
Woellert, K., Ehrenfreund, P., Ricco, A. J., & Hertzfeld, H. (2011). Cubesats: Cost-effective science and technology platforms for emerging and developing nations. Advances in Space Research, 47(4), 663–684. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2010.10.009
-
Wu, L., Beard, B. L., Roden, E. E., & Johnson, C. M. (2009). Influence of pH and dissolved Si on Fe isotope fractionation during dissimilatory microbial reduction of hematite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(19), 5584–5599. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2009.06.026
-
Wu, L., Beard, B. L., Roden, E. E., & Johnson, C. M. (2011). Stable Iron Isotope Fractionation Between Aqueous Fe(II) and Hydrous Ferric Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol., 45(5), 1847–1852. doi:10.1021/es103171x
-
Wu, L., Beard, B. L., Roden, E. E., Kennedy, C. B., & Johnson, C. M. (2010). Stable Fe isotope fractionations produced by aqueous Fe(II)-hematite surface interactions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(15), 4249–4265. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2010.04.060
-
Xu, H., Chen, T., & Konishi, H. (2010). HRTEM investigation of trilling todorokite and nano-phase Mn-oxides in manganese dendrites. American Mineralogist, 95(4), 556–562. doi:10.2138/am.2010.3211
-
Yang, Y., Sahai, N., Romanek, C. S., & Chakraborty, S. (2012). A computational study of Mg2+ dehydration in aqueous solution in the presence of HS− and other monovalent anions – Insights to dolomite formation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 88, 77–87. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.018
-
Zhang, F., Xu, H., Konishi, H., Shelobolina, E. S., & Roden, E. E. (2012). Polysaccharide-catalyzed nucleation and growth of disordered dolomite: A potential precursor of sedimentary dolomite. American Mineralogist, 97(4), 556–567. doi:10.2138/am.2012.3979
-
Zhao, W., Song, Z., Jiang, H., Li, W., Mou, X., Romanek, C. S., … Zhang, C. L. (2011). Ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in Kamchatka Hot Springs. Geomicrobiology Journal, 28(2), 149–159. doi:10.1080/01490451003753076
- Bryson, K.L., Peeters, Z., Salama, F., Foing, B.H., Ehrenfreund, P., Ricco, A.J., Breitfellner, M., Jessberger, E., Bischoff, A. & Robert, F. (2011). Ground Control Monitoring for the Organics Experiment on the EXPOSE-R Facility on the International Space Station. NASA Laboratory Astrophysics Workshop.
- Bryson, K.L., Peeters, Z., Salama, F., Foing, B.H., Ehrenfreund, P., Ricco, A.J., Breitfellner, M., Jessberger, E., Bischoff, A. & Robert, F. (2011, In Press). Ground Control Monitoring for the Organics Experiment on the EXPOSE-R Facility on the International Space Station. NASA Laboratory Astrophysics Workshop,.
- Chakraborty, S., Romanek, C.S. & Moecher, D. (2011). Whole-rock geochemistry, mineralogy, petrography and thermometry of an L6 chondrite from Pembina country,. GSA. North Dakota.
- Christensen, J., Kohl, I. & Coleman, M. (2011). Triple oxygen isotope data characterize oxidation processes that produce sulfate on Earth (and Mars?). AGU Fall meeting 2011 Abstracts.
- Doglioni, C., Pignatti, J. & Coleman, M. (2011, In Review). The effect of the inner core on life on the surface of the Earth. Terra Nova.
- Ehrenfreund, P. & Westall, F. (2011, In Press). Astrobiology experiments in Low Earth Orbit [Book Chapter]. Laboratory Science with Space Data, ULISSE Book. Springer Verlag.
- Ehrenfreund, P. & Westall, F. (2011, In Press). Astrobiology experiments in Low Earth Orbit [Book Chapter]. Laboratory Science with Space Data. Springer Verlag.
- Ehrenfreund, P., Ricco, A.J., Quinn, R., Bramall, Bryson, K., Chittenden, J., Cook, A., Mancinelli, R., Mattioda, A., Minelli, G., Nicholson, W., Santos, O., Squires, D., Kitts, C., Rasay, R., Young, A. & Ames, O-S. (2011). The O/OREOS mission – Astrobiology data collected in low Earth orbit. 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference.
- Ehrenfreund, P., Ricco, A.J., Quinn, R., Bramall, Bryson, K., Chittenden, J., Cook, A., Mancinelli, R., Mattioda, A., Minelli, G., Nicholson, W., Santos, O., Squires, D., Kitts, C., Rasay, R., Young, A. & Ames, O-S. (2011). The O/OREOS mission – Astrobiology data collected in low Earth orbit. 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference.
- Ehrenfreund, P., Ricco, A.J., Quinn, R., Bramall, N., Bryson, K., Chittenden, J., Cook, A., Mancinelli, R., Mattioda, A., Minelli, G., Nicholson, W., Santos, O., Squires, D., Friedericks, C., Kitts, C., Rasay, R. & Ames, O-S. (2011). O/OREOS: A successful mission of NASA’s Astrobiology Small Payload Program. 62nd International Astronautical Congress. Cape Town, SA.
- Ehrenfreund, P., Röling, W.F.M., Thiel, C.S., Quinn, R., Sephton, M.A., Stoker, C., Kotler, M., Direito, S.O.L., Martins, Z., Orzechowska, G.E., Kidd, R.D. & Foing, B.H. (2011). Habitability studies in preparation for future Mars missions. 62nd International Astronautical Congress. Cape Town, SA.
- Ehrenfreund, P., Spaans, M. & Holm, N. (2011). The evolution of organic matter in space, Philosophical Transactions A: Royal Society Meeting The detection of extraterrestrial life and the consequences for science and society. Phil. Trans. R. Soc, A 2011(369): 538-554.
- Ehrenfreund, P., Spaans, M. & Holm, N. (2011). The evolution of organic matter in space. Philosophical Transactions A: Royal Society Meeting: The detection of extraterrestrial life and the consequences for science and society. Phil. Trans. R. Soc, A(369): 538-554.
- Foing, B.H., Thiel, C., Direito, S., Ehrenfreund, P., Rolin, W., Martins, Z., Sephton, M., Stoker, C., Zhavaleta, J., Orzechowska, G., Kidd, R., Quinn, R., Kotler, M. & Team, I.E.2. (2011). Astrobiology and habitability studies supporting Mars research and missions. 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference.
- Foing, B.H., Thiel, C., Direito, S., Ehrenfreund, P., Roling, W., Martins, Z., Sephton, M., Stoker, C., Zhavaleta, J., Orzechowska, G., Kidd, R., Quinn, R., Kotler, M. & Team, E.M. (2011). Astrobiology and habitability studies supporting Mars research and missions. 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract.
- Greiner, E., Kumar, K., Giuffre, A., Sumit, M., Pedersen, J., Cleaves, J., Dworkin, J. & Sahai, N. (In Preparation). Adsorption of L-Glutamate and L-Aspartate from solution onto γ-Al2O3 surfaces. Langmuir.
- Huberty, J., Konishi, H., Fournelle, J., Heck, P., Valley, J. & Xu, H. (2010a). Silician Magnetite from the Dales Gorge Banded Iron Formation. Goldschmidt Conference. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Suppl, 74(A434).
- Huberty, J., Konishi, H., Fournelle, J., Heck, P., Valley, J. & Xu, H. Silician Magnetite from the Dales Gorge Banded Iron Formation. Goldschmidt Conference. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Suppl, 74(A434).
- Huberty, J.M., Kita, N.T., Heck, P.R., Kozdon, R., Fournelle, J.H., Xu, H. & Valley, J.W. (2010). In situ δ18O analyses in quartz and magnetite from the Dales Gorge BIF. 5th International Archean Symposium.
- Huberty, J.M., Kita, N.T., Heck, P.R., Kozdon, R., Fournelle, J.H., Xu, H. & Valley, J.W. (2010c). In situ δ18O analyses in quartz and magnetite from the Dales Gorge BIF. 5th International Archean Symposium.
- Hurowitz, J.e. & A. (2011). In-Situ K-Ar Geochronology: Age Dating for Solar System Sample Return Selection” and its Importance to Solar System Sample Return Missions for the Future of Planetary Sciences. 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference.
- Hurowitz, J.e. & A. (2011). In-situ Potassium-Argon geochronology using fluxed fusion and a double spike. NASA Tech Brief, # 48099.
- Johnson, C. (2011, Submitted). Archean Isotopic Records: Paleo-Ocean Proxies or Microbial Cycling? Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull.
- Kita, N.T., Huberty, J.M. & Valley, J.W. (2010). Improvement of SIMS oxygen isotope analyses on magnetite, 20th V.M. Goldschmidt Conference. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Suppl, 74(A521).
- Kita, N.T., Huberty, J.M., Kozdon, R., Beard, B.L. & Valley, J.W. (2010). High precision SIMS oxygen, sulfur and iron stable isotope analyses of geological materials: Accuracy, surface topography and crystal orientation. SIMS XVII Proceedings, Surface and Interface Analysis.
- Kitts, C., Rasay, R., Bica, L., Mas, I., Neumann, M., A.Young, Minelli, G., Ricco, A., Stackpole, E., Agasid, E., Beasley, C., Friedericks, C., Squires, D., Ehrenfreund, P., Nicholson, W., Mancinelli, R., Santos, O., Quinn, R., Bramall, N., Mattioda, A., A.Cook, Chittenden, J., Bryson, K., Piccini, M. & Parra, M. (2011). Initial On-Orbit Engineering Results from the O/OREOS Nanosatellite. 25th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites.
- Kozdon, R., Kita, N., Huberty, J., Fournelle, J. & Valley, J.W. (2009). In situ Sulfur Isotope Analysis of Sphalerite by SIMS: Precision vs. Accuracy. Eos Trans. AGU Fall Meet. Suppl.
- Kozdon, R., Kita, N.T., Huberty, J.M., Fournelle, J.H., Williford, K. & Valley, J.W. (2010). In situ sulfur isotope analysis of sphalerite and other sulfides by SIMS: Precision vs. Accuracy. AbSciCon.
- Kuhlman, K.R., Behar, A., Jones, J., Boston, P., Jeffrey Antol, J., Hajos, G., Kelliher, W., Coleman, M., Crawford, R., Rothschild, L., Buehler, M., Bearman, G., Wilson, D.W. & McKay, C.P. (2010). Tumbleweed: a new paradigm for surveying Mars for in-situ resources. In: Badescu, V. (Eds.). Mars, Prospective Energy and Material Resources. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
- Kuhlman, K.R., Behar, A., Jones, J., Boston, P., Jeffrey Antol, J., Hajos, G., Kelliher, W., Coleman, M., Crawford, R., Rothschild, L., Buehler, M., Bearman, G., Wilson, D.W. & McKay, C.P. (2010). Tumbleweed: a new paradigm for surveying mars for in-situ resources. The Aerospace Division of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Earth & Space 2010 Conference papers of Earth and Space.
- Li, W., Beard, B. & Johnson, C. (2012, In Press). U-Th-Pb isotope data indicate Phanerozoic age for oxidation of 3.4 Ga basalts from Marble Bar, Pilbara Craton, NW Australia. Earth and Planetary Sciences Letters,.
- Li, W., Beard, B.L., Van Kranendonk, M. & Johnson, C. (2012). U-Th-Pb isotope data and stable Fe isotopes indicate formation of the 3.4 Ga Marble Bar Chert from anoxic seawater. Nature.
- Li, W., Johnson, C. & Beard, B. (20111). U-Th-Pb isotopic constraints on the oxidation age of 3.4 Ga basalts from Marble Bar, Pilbara Craton, NW Australia. AGU Fall Meeting.
- Minelli, G., Ricco, A.J., Beasley, C., Hines, J., Agasid, E., Yost, B., Squires, D., Friedericks, C., Piccini, M., Defou, G., McIntyre, M., Ricks, R., Parra, M., Diaz-Aguado, M., Timucin, L., Henschke, M., Lera, M., Tan, M., Cohen, M., Ronzano, K., Luzzi, E., Mai, N., Schooley, A., Ly, D., Stackpole, E., Lin, J., Tucker, J., Ehrenfreund, P., Mancinelli, R., Mattioda, A., Nicholson, W., Quinn, R., Santos, O., Bramall, N., Bryson, K., Chittenden, J., Taylor, C., Cook, A. & Landis, D. (2010). O/OREOS Nanosatellite: A Multi-Payload Technology Demonstration. 24th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites. Logan, Utah.
- Minelli, G., Ricco, A.J., Beasley, C., Hines, J., Agasid, E., Yost, B., Squires, D., Friedericks, C., Piccini, M., Defouw, G., McIntyre, M., Ricks, R., Parra, M., Diaz-Aguado, M., Timucin, L., Henschke, M., Lera, M., Tan, M., Cohen, M., Ronzano, K., Luzzi, E., Mai, N., Schooley, A., Ly, D., Stackpole, E., J. Lin, J.T., Ehrenfreund, P., Mancinelli, R., Mattioda, A., Nicholson, W., Quinn, R., Santos, O., Bramall, N., Bryson, K., Chittenden, J., Taylor, C., Cook, A. & Landis, D. (2010). O/OREOS Nanosatellite: A Multi-Payload Technology Demonstration. h Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites. Logan, Utah.
- Oleson, T.A., Wesolowski, D.J., Dura, J.A., Majkrzak, C.F., Giuffre, A.J. & Sahai, N. (2011, In review). Neutron reflectvity study of phosphatidylcholine bilayers on sapphire (110). J. Colloid. Interf. Sci.
- Report, C. (2011). International Earth-based research program as a stepping stone for global space exploration. COSPAR. Paris.
- Rummel, J.D. & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). Extending the Outer Space Treaty to Protect Planetary Environments. 62nd International Astronautical Congress. Cape Town, SA.
- Shelobolina, E., Xiong, M.Y. & Roden, E.E. (2011). Isolation of iron-cycling organisms from an illite-smectite rich subsoil. Frontiers in Chemical Microbiology, Manuscript in preparation.
- Shelobolina, E., Xiong, M.Y., Kennedy, D.W. & Roden, E.E. (2011). Microbial agents of Fe-phyllosilicate redox metabolism in Hanford 300 Area sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol, Manuscript in preparation.
- Shen, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, F., Kemp, J., Szlufarska, I. & Xu, H. (2011). Modeling the effect of dissolved hydrogen sulfide on Mg2+-water complex on dolomite {104} surface. Annual Meeting of the Geological Society of America. Minneapolis.
- Sinha, M.P., Hecht, M.H. & Hurowitz, J. (2011). In-Situ Geochemical Analysis and Age Dating of Rocks using Laser Ablation-Miniature Mass Spectrometer (LA-MMS). NASA Tech Brief, # 48250.
- Temperature-dependent Mg isotope fractionation during precipitation of inorganic calcite under laboratory conditions.
- Thiel, C., Ehrenfreund, P., Pletser, V., Foing, B.H. & Ullrich, O. (2011). Analysis of microbial diversity by PCR in a Mars analogue environment – the Mars Desert Research Station. 62nd International Astronautical Congress. Cape Town, SA.
- Ushikubo, T., Kita, N.T. & Valley, J.W. (2010). Recent Progress of Small Spot Oxygen Isotope Analysis at WiscSIMS. Goldschmidt Conference. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Suppl, 74(A1067).
- Valley, J. (2010). Magmatic Zircons: Evolution of δ18O Through Time – Revisited in situ. Goldschmidt Conference. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Suppl, 74(A1069).
- Valley, J.W., Grimes, C.B., Bouvier, A-., Ushikubo, T., Ortiz, D.M., Cavosie, A.J. & Wilde, S.A. (2010). Improvement of SIMS Oxygen Isotope Analyses on Magnetite. Goldschmidt Conference. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Suppl, 74(A521).
- Walter, N., Smith, T., Worms, J.C., Rummel, J., McKay, C. & Ehrenfreund, P. (2011). International Earth-based research and technology program as a stepping stone for global space exploration. 62nd International Astronautical Congress. Cape Town, SA.
- Williford, K., Van Kranendonk, M.J., Ushikubo, T., Kozdon, R., Spicuzza, M.J. & Valley, J.W. (2011). Transitional oxygenation recorded in the Paleoproterozoic Turee Creek Group, Western Australia. Goldschmidt Conference.
- Williford, K.H., Ushikubo, T., Kozdon, R., Van Kranendonk, M.J. & Valley, J.W. (2010). ) In situ sulfur isotope evidence for low atmospheric oxygen and high seawater sulfate in Proterozoic glaciogenic sediments of the Turee Creek Group, Western Australia. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 42(5).
- Williford, K.H., Ushikubo, T., Kozdon, R., Van Kranendonk, M.J. & Valley, J.W. (2010). In situ sulfur isotope evidence for low atmospheric oxygen and high seawater sulfate in Proterozoic glaciogenic sediments of the Turee Creek Group, Western Australia. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 42(397).
- Williford, K.H., Ushikubo, T., Lepot, K., Hallmann, C., Spicuzza, M.J., Eigenbrode, J.L., Summons, R.E. & Valley, J.W. (2011). Spatially resolved, in situ carbon isotope analysis of Archean organic matter. American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting.
- Williford, K.H., Van Kranendonk, M.J., Ushikubo, T., Kozdon, R. & Valley, J.W. (2011). Transitional oxygenation recorded in the Paleoproterozoic Turee Creek Group Western Australia. Goldschmidt Conference. Mineralogical Magazine, 75.
- Xu J., H., W., J. & Sahai, N. (2011). Evolution of bacterial biofilms as armor against mineral toxicity. Astrobiology.
- Xu, H. (2010). Synergistic roles of microorganisms in mineral precipitates associated with deep sea methane seeps. In: Barton, L.L., Mandl, M. & Loy, A. (Eds.). Geomicrobiology: Molecular and Environmental Perspective. Springer.
- Xu, J., Sahai, N. & A, S.M.A. (In Preparation). Formation mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in aqueous suspensions of oxide minerals: Implications for organic and cellular evolution on early Earth and extra-terrestrial worlds. Astrobiology.
- Zhang, F., Xu, H., Konishi, H., Yan, C., Teng, H. & Roden, E.E. (2011). Aqueous sulfide-catalyzed nucleation and growth of disordered dolomite at room temperature. Annual Meeting of the Geological Society of America. Minneapolis.
- Zhu, C., Xu, J., Hickey, W.J. & Sahai, N. (2011, In Preperation). Role of cell wall structure and extra-cellular polymeric substances (EPS) in shielding against specific mineral toxicity: Implications for cell surface evolution. Astrobiology.