2011 Annual Science Report
 NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory - Titan
Reporting | SEP 2010 – AUG 2011
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory - Titan
Reporting | SEP 2010 – AUG 2011
Task 1.1.1 Models of the Internal Dynamics: Formation of Liquids in the Subsurface and Relationships With Cryovolcanism
Project Summary
The internal and external geologic evolution of Titan was investigated so as to constrain the environment in which organic evolution has proceeded over time.
Project Progress
Deputy PI Jonathan Lunine in conjunction with colleague Julie Castillo-Rogez last year demonstrated that the moment of inertia of Titan could be explained with a hydrated silicate core. This model became even more promising with indications that to-be published gravity data on Titan suggests an internal compressibility possibly larger than what an internal ammonia-water ocean under a thin crust could provide. This motivated Lunine to further investigate, again in conjunction with Castillo-Rogez, how such a hydrated silicate model could work, in particular, how to slow the onset of the dehydrate by leaching radioactive elements from the core into the ocean early on. The results, presented at the 2011 DPS meeting (joint with EPSC) in France in October, included a plausible mechanism for leaching, solubility studies, and an inventory of the decay products showing that the outgassed argon-40 is larger than but consistent with that observed to be present in Titan’s atmosphere. The work also provides a mechanism for reinitiating geologic activity on Titan during the last ½-1 billion years of its history, consistent with impact crater counting and recent isotopic studies from Cassini (reported at the same DPS meeting). Indeed, the mechanism of renewed geologic activity involves warm water destabilizing methane clathrate to release methane, and possibly delaminate ethane clathrate from the base of the crust to sequester it in the deep interior.
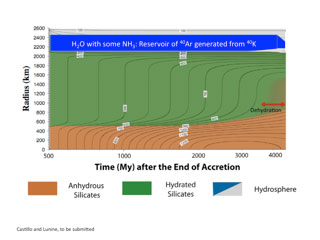
Figure 1: Evolution of the proposed hydrated silicate model, with a base map of temperature contours versus radius (ordinate) and time (abscissa) (from Castillo-Rogez and Lunine, 2010). The potassium-40 is leached into the ocean prior to dehydration; dehydration’s onset dilutes the ocean of ammonia but injects warm water from the core into the upper layers.
-
PROJECT INVESTIGATORS:
-
PROJECT MEMBERS:
Julie Castillo-Rogez
Collaborator
-
RELATED OBJECTIVES:
Objective 1.1
Formation and evolution of habitable planets.
Objective 2.2
Outer Solar System exploration
Objective 3.1
Sources of prebiotic materials and catalysts
Objective 3.2
Origins and evolution of functional biomolecules
Objective 3.3
Origins of energy transduction
