2010 Annual Science Report
 Georgia Institute of Technology
Reporting | SEP 2009 – AUG 2010
Georgia Institute of Technology
Reporting | SEP 2009 – AUG 2010
Molecular Resurrection of the Ancestral Peptidyl Transferase Center
Project Summary
We have resurrected, reconstructed, and are currently reconstituting a model of the a-PTC (ancestral Peptidyl Transferase Center), which we believe to have evolved around 4 billion years ago. The proposed a-PTC contains 644 nucleotides of ancestral ribosomal RNA (a-rRNA), five ancestral ribosomal peptides (a-rPeptides), and inorganic cations. Here we show data of the a-rRNA folding with Mg2+ and a-rPeptides
Project Progress
We have previously shown the successful resurrection and reconstruction of a model of the native ancestral rRNA (a-rRNA), which has 644 nucleotides, in silico and in vitro. Our current efforts are to (i) characterize the a-rRNA folding and assembly with five ancestral ribosomal peptides (a-rPeptides) and Mg2+ to form the ancestral Peptidyl Transferase Center (a-PTC) by gel mobility shift assay, (ii) characterize the enzymatic activity of the a-PTC by the “fragment assay” 1,2, and ultimately, (iii) determine the 3D structure of the a-PTC by X-ray diffraction.
The a-rRNA with magnesium ions. Four recurrent rRNA-Mg2+ complexes (Mg2+-microclusters D1- D4) 3 are found to provide the framework for the PTC in the large subunit (LSU) of H. marismortui 4 and T. thermophilus 5. Three Mg2+-microclusters (D1, D2, and D4) along with other highly coordinated Mg2+ ions are considered to be critical for the a-rRNA folding6,7. Here we study the a-rRNA folding with different Mg2+ concentrations by gel mobility shift assay (Figure 1). The result shows that in the absence of Mg2+, the a-rRNA has three different conformations at equilibrium. By increasing the Mg2+ concentration, the bottom band begins to shift (at 100 μM Mg2+) toward the middle band, then to the top band at higher Mg2+ concentrations. At the highest Mg2+ concentration (5 mM, in this study), most of the conformations are shifted to the top, showing the a-rRNA folding is affected by the Mg2+.
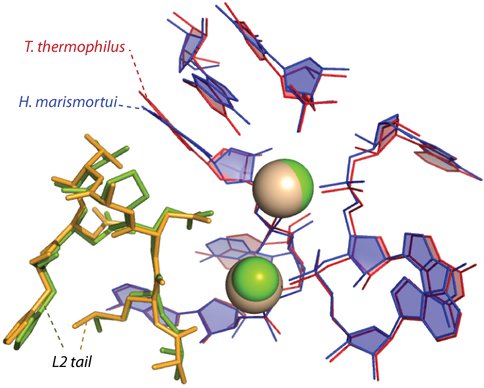
The a-rRNA with the five a-rPeptides. Several ribosomal proteins within the 50S ribosome are considered to be essential to maintain the enzymatic activity of the ribosome 8,9. We have identified five ribosomal peptides (a-rPeptides L2, L3, L4, L15, and L22) that we think are ancient and important to a-PTC folding and function. We studied the a-rRNA folding in the absence of Mg2+ ions for each a-rPeptide by gel mobility shift assay. We see the mobility shift on the a-rRNA with each a-rPeptide, except for L2. Band shifting of the a-rRNA with the L2 takes place only in the presence of Mg2+ ions (Figure 2A). This suggests the a-rRNA folding with the a-rPeptide L2 requires Mg2+ ions where we see the L2 tail is intimately complexed with the ribosomal RNA and the Mg2+-microcluster in the three-dimensional structures of the ribosomes (Figure 2B) 3. Overall, the band shifting patterns of the a-rRNA with each a-rPeptide are different than the a-rRNA with Mg2+ ions and the a-rRNA with spermine (data not shown). These results indicate all the a-rPeptides affect the a-rRNA folding.
(1) Schmeing, T. M.; Seila, A. C.; Hansen, J. L.; Freeborn, B.; Soukup, J. K.; Scaringe, S. A.; Strobel, S. A.; Moore, P. B.; Steitz, T. A. Nat Struct Biol. 2002, 9, 225.
(2) Anderson, R. M.; Kwon, M.; Strobel, S. A. J Mol Evol. 2007, 64, 472.
(3) Hsiao, C.; Williams, L. D. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3134.
(4) Ban, N.; Nissen, P.; Hansen, J.; Moore, P. B.; Steitz, T. A. Science 2000, 289, 905.
(5) Selmer, M.; Dunham, C. M.; Murphy, F. V.; Weixlbaumer, A.; Petry, S.; Kelley, A. C.; Weir, J. R.; Ramakrishnan, V. Science 2006, 313, 1935.
(6) Hsiao, C.; Tannenbaum, M.; VanDeusen, H.; Hershkovitz, E.; Perng, G.; Tannenbaum, A.; Williams, L. D. In Nucleic Acid Metal Ion Interactions; Hud, N., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, 2008, p in press.
(7) Hsiao, C.; Mohan, S.; Kalahar, B. K.; Williams, L. D. Mol Biol Evol 2009.
(8) Schulze, H.; Nierhaus, K. H. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 609.
(9) Khaitovich, P.; Mankin, A. S.; Green, R.; Lancaster, L.; Noller, H. F. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1999, 96, 85.
Figure 1. The a-rRNA folding with Mg2+. Shown is the a-rRNA folding with different magnesium concentrations on a 5% acrylamide gel. The Mg2+ concentrations in each lane are: Lane 1 (no Mg2+); Lane 2: 1 μM; Lane 3: 50 μM; Lane 4: 100 μM, Lane 5: 500 μM, Lane 6: 1 mM, Lane 7: 5 mM.
Figure 2A. The L2-Mg2+-rRNA complex and folding. Shown is the mobility shift of the a-RNA with the a-rPeptide L2 and Mg2+ ions on a 5% acrylamide gel. Lane 1 is a-rRNA only. Lane 2 contains 10 μM of Mg2+. Lanes 3 through 6 are the a-rRNA folding with the a-rPeptide L2 at the molar ratio of 1, 5, 20, and 40 in the absence of Mg2+. Lanes 7 through 10 are the a-rRNA folding with the a-rPeptide L2 at the molar ratio of 1, 5, 20, and 40 in the presence of 10 μM Mg2+.
Figure 2B. An ancestral scaffold for the PTC of archaea and bacteria where it shows the a-rPeptide L2 is complexed with the Mg2+ and the a-rRNA. The positions of the a-rRNA, the magnesium ions, and the a-rPeptide have been conserved over billions of years of evolution.
Publications
-
Hsiao, C., & Williams, L. D. (2009). A recurrent magnesium-binding motif provides a framework for the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center. Nucleic Acids Research, 37(10), 3134–3142. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp119
-
Hsiao, C., Mohan, S., Kalahar, B. K., & Williams, L. D. (2009). Peeling the Onion: Ribosomes Are Ancient Molecular Fossils. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 26(11), 2415–2425. doi:10.1093/molbev/msp163
- Anderson, R.M., Kwon, M. & Strobel, S.A. (2007). Toward ribosomal RNA catalytic activity in the absence of protein. J Mol Evol, 64(4): 472-83.
- Ban, N., Nissen, P., Hansen, J., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. (2000). The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science, 289(5481): 905-920.
- Hsiao, C., Tannenbaum, M., VanDeusen, H., Hershkovitz, E., Perng, G., Tannenbaum, A. & Williams, L.D. (2008). Complexes of Nucleic Acids with Group I and II Cations. In: Hud, N. (Eds.). Nucleic Acid Metal Ion Interactions. London: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
- Khaitovich, P., Mankin, A.S., Green, R., Lancaster, L. & Noller, H.F. (1999). Characterization of functionally active subribosomal particles from Thermus aquaticus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(1): 85-90.
- Schmeing, T.M., Seila, A.C., Hansen, J.L., Freeborn, B., Soukup, J.K., Scaringe, S.A., Strobel, S.A., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. (2002). A pre-translocational intermediate in protein synthesis observed in crystals of enzymatically active 50S subunits. Nat Struct Biol, 9(3): 225-30.
- Schulze, H. & Nierhaus, K.H. (1982). Minimal set of ribosomal components for reconstitution of the peptidyltransferase activity. EMBO Journal, 1(5): 609-13.
- Selmer, M., Dunham, C.M., Murphy, F.V., Weixlbaumer, A., Petry, S., Kelley, A.C., Weir, J.R. & Ramakrishnan, V. (2006). Structure of the 70S ribosome complexed with mRNA and tRNA. Science, 313(5795): 1935-42.
-
PROJECT INVESTIGATORS:
-
PROJECT MEMBERS:
Chiaolong Hsiao
Postdoc
Jessica Bowman
Research Staff
Eric O'Neill
Research Staff
Michelle Williams
Research Staff
Ava Afshar
Undergraduate Student
Jason Murray
Undergraduate Student
Jessica Peters
Undergraduate Student
Catherine Trippe
Undergraduate Student
-
RELATED OBJECTIVES:
Objective 3.2
Origins and evolution of functional biomolecules