2009 Annual Science Report
 University of Hawaii, Manoa
Reporting | JUL 2008 – AUG 2009
University of Hawaii, Manoa
Reporting | JUL 2008 – AUG 2009
Comet Kopff Thermal Modelling
Project Summary
We examine the behavior of a typical comet, designated 22P/Kopff, as it orbits the Sun. When the comet approaches the minimum distance form the Sun, a heat wave penetrates from the surface inwards. This input of heat causes the material to change. These changes invoke an outflow of various gases and solids, which are responsible for the patterns of activity, visible as a coma and tail.
Project Progress
This project involves quasi-3D modeling of a typical Jupiter-family comet, Comet 22P/Kopff. We study the dust activity and its connection to internal thermal evolution. The outstanding feature emerging from the quasi-3D thermal simulations is that even at relatively high cometocentric latitudes the nucleus will develop a complex pattern of volatile stratification with depth. Comet 22P/Kopff is evolved through various initial models, in order to try and explain its peculiar dust activity near perihelion, as observed and modeled by Finson-Probstein dust-dynamical models.
Optical CCD observations were obtained during four nights, between 1989-1992, using the UH 2.2-m telescope on Mauna Kea. These were used to make deep composite images to search for dust activity (A. R. Zenn, private communication).
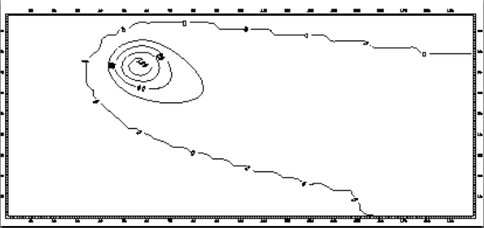
Dust-dynamical models were developed by Zenn & Meech for the available observations datasets, using the Finston-Probstein method (F-P). This method models a cometary tail in order to determine onset and cessation of emission, particle production rates, sizes, and velocities. Three of the models (1989 observations) corresponded to pre-perihelion activity, with a sunward emission function. The latter model (1992 observations) corresponded to post-perihelion activity and displayed an interesting result with emission directed from a specific location (“jet”) on the nucleus (see Fig. 1).
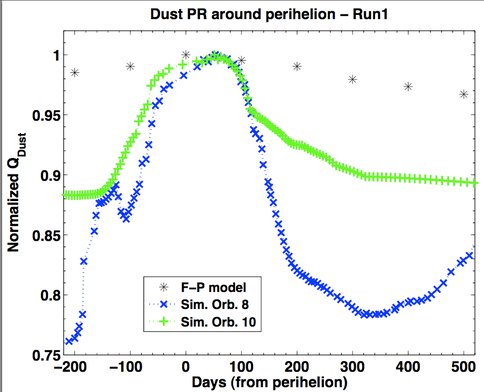
Thermal evolution models of the nucleus of 22P/Kopff were calculated, by means of a quasi-3D code (Prialnik et al. 2004).This code takes into account diurnal and latitudinal variations, but neglects lateral heat conduction. For these specific models we have focused on the location of the directed emission, as derived from the dust-dynamical modeling (see Fig. 2). We examine the dependence of the activity on a few key parameters by following the outgassing of volatiles, ejection of dust and heat transport inside the nucleus.
Figure 1. Figure 1 – Contour plot of the best-fit model for the Jan. 6, 1992 image of Kopff. North is up and east is to the left.
Figure 2. Figure 2 – Dust production rates for the two most akin orbits, for a model of the nucleus of Kopff. production rates are normalized to the maximum emission at each orbit. Time is presented in days relative to perihelion and only near-perihelion parts of the orbit are shown. We compare results of the dust-dynamical modeling (black “*” 's), the earlier orbit (blue “x” 's) and the later orbit (green “+” 's).
-
PROJECT INVESTIGATORS:
-
PROJECT MEMBERS:
Karen Meech
Project Investigator
Gal Sarid
Postdoc
Anthony Zenn
Graduate Student
-
RELATED OBJECTIVES:
Objective 2.2
Outer Solar System exploration